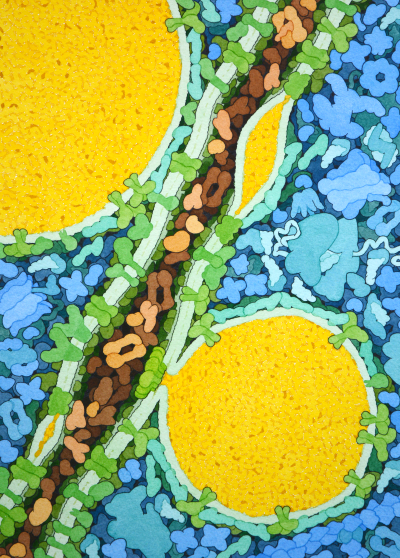
Molecular Landscapes by David S. Goodsell
Lipid Droplets, 2019
Acknowledgement: Illustration by David S. Goodsell, RCSB Protein Data Bank. doi: 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/goodsell-gallery-017
Lipids such as fats and cholesterol are stored in large droplets inside cells. This painting shows how these droplets are formed. The lipids (yellow) are inserted between the two leaflets of a lipid bilayer of the endoplasmic reticulum (running diagonally through the picture), and the droplet buds out from the surface. The protein seipin (PDB entries 6mlu, 6ds5), seen at the narrow connection between the lower droplet and the ER, assists with the process.