Peak Performance
the structural biology of athletics and well-being
Athletes require bodies that are the best that is possible, all the way from molecules to muscles. By understanding the structure and function of our molecules, athletes can ensure that they are performing at their peak. This knowledge also informs the ways that we all can live our best lives, at all stages of our lives.
Molecule of the Month Articles (38)
 |
Acetohydroxyacid Synthase
In plants, AHAS performs the first step in synthesis of three essential amino acids, making it an effective target for herbicides. |
 |
Adrenergic Receptors
Adrenaline stimulates a G-protein-coupled receptor, priming us for action |
 |
Alcohol Dehydrogenase
Alcohol dehydrogenase detoxifies the ethanol we drink |
 |
Anabolic Steroids
Anabolic steroids like testosterone are among the most common performance enhancing drugs |
 |
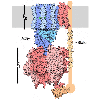
Angiotensin and Blood Pressure
Many medications for controlling high blood pressure inhibit the action of the peptide hormone angiotensin. |
 |
ATP Synthase
ATP synthase links two rotary motors to generate ATP |
 |
Calcium Pump
Atomic structures have captured the calcium pump in action |
 |
Carbonic Anhydrase
Carbonic anhydrase solubilizes carbon dioxide gas so we can breathe it out |
 |
Catalase
Catalase protects us from dangerous reactive oxidizing molecules |
 |
Circadian Clock Proteins
Circadian clock proteins measure time in our cells |
 |
Citric Acid Cycle
Eight enzymes form a cyclic pathway for energy production and biosynthesis |
 |
Complex I
A proton-pumping protein complex performs the first step of the respiratory electron transport chain |
 |
Cytochrome c Oxidase
Cytochrome oxidase extracts energy from food using oxygen |
 |
Estrogen Receptor
Estrogen binds to receptors in the nucleus and affects key genes in development |
 |
Fatty Acid Synthase
Fatty acids are constructed in many sequential steps by a large protein complex |
 |
Glycogen Phosphorylase
Glycogen phosphorylase releases sugar from its cellular storehouse |
 |
Glycolytic Enzymes
The ten enzymes of glycolysis break down sugar in our diet |
 |
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone brings together two copies of its cellular receptor |
 |
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin uses a change in shape to increase the efficiency of oxygen transport |
 |
Hypoxia-Inducible Factors
HIF-α is a molecular switch that responds to changing oxygen levels. |
 |
Lactate Dehydrogenase
Our cells temporarily build lactate when supplies of oxygen are low |
 |
Lead Poisoning
Lead ions poison proteins throughout the body, blocking their normal function. |
 |
Leptin
Problems with the appetite-controlling hormone leptin can lead to obesity |
 |
Monellin
Monellin and other supersweet proteins trick our taste receptors. |
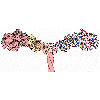 |
Myosin
Molecular motors fueled by ATP power the contraction of muscles |
 |
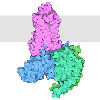
Nicotine, Cancer, and Addiction
Nicotine causes addiction by interacting with receptors in the brain |
 |
Odorant Receptors
Our sense of smell relies on odorant receptors that recognize specific scents. |
 |
Opioid Receptors
Morphine and other opioid drugs bind to receptors in the nervous system, controlling pain |
 |
Oxidosqualene Cyclase
Oxidosqualine cyclase forms the unusual fused rings of cholesterol molecules |
 |
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex
A huge molecular complex links three sequential reactions for energy production |
 |
Respiratory Supercomplex
In our mitochondria, three electron-transport complexes assemble into a supercomplex. |
 |
Rhodopsin
In our eyes, rhodopsin uses the molecule retinal to see light |
 |
S-Nitrosylated Hemoglobin
Nitric oxide is attached to a conserved cysteine in hemoglobin and then released to control the flow of blood. |
 |
Serotonin Receptor
Serotonin receptors control mood, emotion, and many other behaviors, and are targets for many important drugs |
 |
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Cells continually pump sodium ions out and potassium ions in, powered by ATP |
 |
Superoxide Dismutase
Superoxide dismutase protects us from dangerously reactive forms of oxygen |
 |
Vitamin D Receptor
Vitamin D helps regulate the use of calcium throughout the body |
 |
Vitamins
Vitamins are essential molecular tools that are obtained through a healthy diet. |
Learning Resources (14)
| G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR)
Paper Model
GPCRs are a large family of membrane-embedded receptors, with structural features that have been preserved through the course of evolution. This model represents the shared structural features of all GPCRs. With the extracellular N-terminus, the protein chain folds to form a bundle of seven transmembrane alpha helices connected by 3 intracellular and 3 extracellular loops with the C-terminus reaching inside the cell.
|
|
 |
2025 Calendar: The Structural Biology of Nutrition
Calendar
The food that we eat contains four major classes of molecules–proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates–as well as many micronutrients like vitamins and minerals. Our bodies contain thousands of different proteins that interact with and utilize these nutrients to build up our bodies and provide the energy we need to live.
|
| 2024 Calendar: Peak Performance
Calendar
Athletes require bodies that perform best, all the way from molecules to muscles. By understanding the structure and function of biomolecules, athletes can ensure that they are performing at their peak. These include molecules that power and control muscle action, molecules that turn food into energy, essential dietary molecules that are required for health, and molecules that protect our bodies under extreme stress and exertion. This knowledge also informs the ways that all of us can live our best lives, at all stages of our lives.
|
|
 |
How do Drugs Work?
Flyer
PDB structures are used to discuss antibiotics and antivirals, chemotherapy, drug metabolism, drugs of signaling proteins, and lifestyle drugs.
|
 |
Insulin and Diabetes
Poster
Structural biology has revealed the details of insulin signaling and how this knowledge is being used to create new and better treatments for diabetes.
|
 |
How Neurons Communicate
Video
The billions of neurons in our nervous system are constantly communicating. The signals they send to each other are responsible for our thoughts, sensations, and actions. Learn how ions, ion channels, receptors, and neurotransmitters work together to enable the neuronal signaling process.
|
 |
Vitamin A and Vision
Video
Learn how vitamin A activates the molecular pathways that are essential for vision.
|
 |
Caffeine and Adenosine: Antagonist and Agonist
Video
This short video uses the example of adenosine and caffeine to introduce two key concepts in pharmacology: the agonist and the antagonist. Both, adenosine, and caffeine molecules bind to adenosine receptors on the neurons. Caffeine, the antagonist, blocks the receptor, while adenosine, the agonist, produces the biological response upon binding.
|
 |
Opioids and Pain Signaling
Video
Pain is one of the most trying experiences of life. On the cellular level it is communicated via special neuronal pathways. On the molecular level, however, pain is communicated like any other sensation, via a set of electrical and chemical signals facilitated by complex molecular machinery. These signals can be modulated by opioids, causing us to feel less pain, or no pain at all. Learn how opioids activate the G-proteins which in turn interact with other proteins to edit the pain signal.
|
 |
Neuronal Signaling and Sodium-Potassium Pump
Video
Explore the concepts of resting and action potentials and the role of sodium-potassium pump in regulating them.
|
| Calcium Pump
Video
The calcium pump moves ions across cell membranes allowing the synchronized contraction of muscle cells.
|
|
| Bound! Protein-drug matching game
Other Resource
Bound! is a card game for students 12 and up, where players compete to match the most drugs to their protein targets.
|
|
 |
Hemoglobin Bean Bag Toss
Other Resource
|
| Exploring the Structural Biology of Health and Nutrition
Article
By understanding the molecular needs of our cells, we can ensure that our bodies operate at peak performance.
|
Goodsell Molecular Landscapes (3)
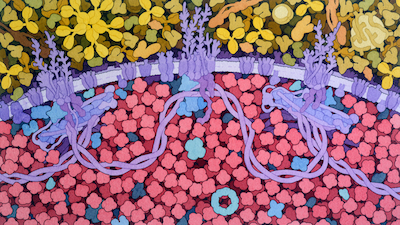 |
Red Blood Cell Cytoskeleton
Cross section through a red blood cell membrane shows the distinctive cytoskeleton
|
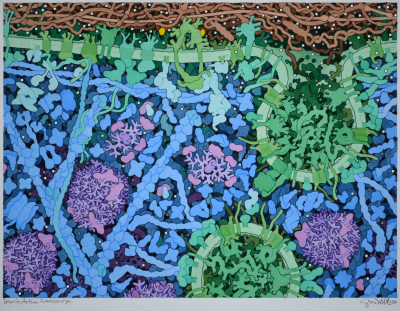 |
Insulin Action
Insulin Action (2016) by David S. Goodsell.
|
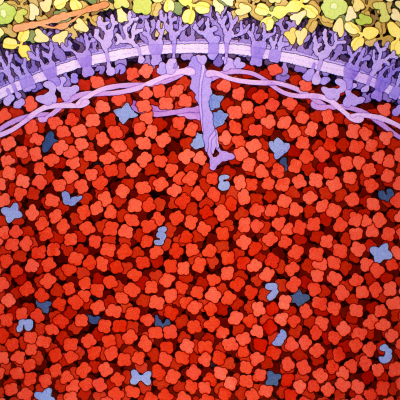 |
Biosites: Red Blood Cell
Biosites: Red Blood Cell (2005) by David S. Goodsell
|



