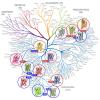
Cellular Signaling
sending and receiving molecular messages
Cells are in constant communication, deciding when to grow, whether dangers are present, and whether they should move to new environments. They talk to one another by sending small messenger molecules, which are received by receptor molecules on their cell surfaces. Atomic structures have revealed both these signaling molecules and their receptors.
Molecule of the Month Articles (58)
 |
Acetylcholine Receptor
The neurotransmitter acetylcholine opens a protein channel, stimulating muscle contraction |
 |
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase stops the signal between a nerve cell and a muscle cell |
 |
Adenylyl Cyclase
Adenylyl cyclase creates second messengers to amplify signals from G-protein coupled receptors |
 |
Adrenergic Receptors
Adrenaline stimulates a G-protein-coupled receptor, priming us for action |
 |
AMPA Receptor
Receptors for the neurotransmitter glutamate in our brain come in several shapes and sizes. |
 |
Anabolic Steroids
Anabolic steroids like testosterone are among the most common performance enhancing drugs |
 |
Anaphase-Promoting Complex / Cyclosome
APC/C guards the checkpoints that regulate key steps in the cell cycle |
 |
Angiotensin and Blood Pressure
Many medications for controlling high blood pressure inhibit the action of the peptide hormone angiotensin. |
 |
ATM and ATR Kinases
Dividing cells use ATM and ATR kinases to respond to DNA damage. |
 |
Auxin and TIR1 Ubiquitin Ligase
The plant hormone auxin controls growth and response to light and gravity |
 |
c-Abl Protein Kinase and Imatinib
Protein kinases are being targeted by new anti-cancer drugs |
 |
Calcium Pump
Atomic structures have captured the calcium pump in action |
 |
Calmodulin
Calcium ions rapidly deliver signals to control processes such as muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and fertilization |
 |
cAMP-dependent Protein Kinase (PKA)
PKA delivers cellular signals by adding phosphates to proteins |
 |
Capsaicin Receptor TRPV1
TRPV1 is an ion channel that senses heat and contributes to pain sensation. |
 |
Cyclin and Cyclin-dependent Kinase
Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases control when cells divide, making them important targets for cancer therapy. |
 |
Cyclooxygenase
Aspirin attacks an important enzyme in pain signaling and blood clotting |
 |
Designer Insulins
Engineered insulins have been developed to improve treatment of diabetes |
 |
Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4
Inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 are used to treat type-2 diabetes |
 |
Epidermal Growth Factor
EGF is part of a family of proteins that controls aspects of cell growth and development |
 |
Estrogen Receptor
Estrogen binds to receptors in the nucleus and affects key genes in development |
 |
G Proteins
G proteins receive signals from cellular receptors and deliver them inside the cell |
 |
Glucagon
Glucagon triggers the release of glucose into the blood, to power cells throughout the body |
| Glucocorticoid Receptor and Dexamethasone
An anti-inflammatory drug has given us a new way to fight the COVID-19 pandemic. |
|
 |
Glutamate-gated Chloride Receptors
The antibiotic ivermectin attacks glutamate-gated chloride channels, paralyzing parasitic worms. |
 |
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone brings together two copies of its cellular receptor |
 |
HER2/neu and Trastuzumab
Trastuzumab monoclonal antibodies targeting HER2 receptors are at the forefront of breast cancer treatment |
 |
Incretins
GLP-1 and GIP are hormones that are released soon after you eat a meal |
 |
Insulin
The hormone insulin helps control the level of glucose in the blood |
 |
Insulin Receptor
The cellular receptor for insulin helps control the utilization of glucose by cells |
 |
Interferons
Interferons mobilize defenses against viral infection |
 |
Leptin
Problems with the appetite-controlling hormone leptin can lead to obesity |
 |
Mechanosensitive Channels
Pressure-sensitive channels open when the internal pressure of a cell gets too high |
 |
Neurotransmitter Transporters
Neurotransmitters are transported out of nerve synapses to end a signal transmission |
 |
Neurotrophins
Neurotrophins guide the development of the nervous system |
 |
Nicotine, Cancer, and Addiction
Nicotine causes addiction by interacting with receptors in the brain |
 |
Nitric Oxide Synthase
Nitric oxide gas is used as a rapid-acting hormone and as a powerful defense |
 |
Odorant Receptors
Our sense of smell relies on odorant receptors that recognize specific scents. |
 |
Opioid Receptors
Morphine and other opioid drugs bind to receptors in the nervous system, controlling pain |
 |
PD-1 (Programmed Cell Death Protein 1)
PD-1 and its ligands are a new target for cancer therapy |
 |
Photoactive Yellow Protein
Researchers use synchrotrons and X-ray lasers to reveal the rapid processes of light sensing. |
 |
Phototropin
Phototrophins sense the level of blue light, allowing plants to respond to changing environmental conditions |
 |
Phytohormone Receptor DWARF14
Some phytohormones mobilize the cell’s protein degradation machinery to regulate plant growth and development. |
 |
Phytosulfokine Receptor
Phytosulfokine and other small peptides deliver signals about growth and development in plants. |
 |
Piezo1 Mechanosensitive Channel
Mechanosensitive ion channels give our cells a sense of touch. |
 |
Potassium Channels
Potassium channels allow potassium ions to pass, but block smaller sodium ions |
 |
RAF Protein Kinases
A single mutation in a RAF protein kinase can help transform a normal cell into a cancer cell. |
 |
Ras Protein
Mutation of the growth-controlling ras protein can lead to cancer |
 |
Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products
RAGE recognizes sugar-modified proteins, contributing to an inflammatory response that plays a role in diabetes |
 |
Rhodopsin
In our eyes, rhodopsin uses the molecule retinal to see light |
 |
Serotonin Receptor
Serotonin receptors control mood, emotion, and many other behaviors, and are targets for many important drugs |
 |
SNARE Proteins
SNARE proteins power the fusion of vesicles with membranes by forming a bundle of alpha helices |
 |
Src Tyrosine Kinase
Growth signaling proteins play an important role in the development of cancer |
 |
Tissue Factor
Tissue factor senses damage to the body and triggers formation of a blood clot |
 |
Two-component Systems
Bacteria respond to their environment with two-component sensing systems. |
 |
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VegF) and Angiogenesis
VegF promotes blood vessel formation (angiogenesis), affecting cancer proliferation, wound healing, and other bodily processes. |
 |
Vitamin D Receptor
Vitamin D helps regulate the use of calcium throughout the body |
 |
Voltage-gated Sodium Channels
Voltage-gated sodium channels transmit signals in a wave through the nervous system. |
Learning Resources (16)
| G Protein-Coupled Receptor (GPCR)
Paper Model
GPCRs are a large family of membrane-embedded receptors, with structural features that have been preserved through the course of evolution. This model represents the shared structural features of all GPCRs. With the extracellular N-terminus, the protein chain folds to form a bundle of seven transmembrane alpha helices connected by 3 intracellular and 3 extracellular loops with the C-terminus reaching inside the cell.
|
|
 |
Insulin
Paper Model
Learn about insulin, a peptide hormone that plays a critical role in our ability to use glucose from the food that we eat
|
 |
Molecular Explorations for 2026
Calendar
This calendar celebrates the work of Janet Iwasa, who creates the Molecule of the Month series for RCSB PDB.
|
 |
Award-winning Illustration of Glutamatergic Synapse
Poster
Molecular view of glutamatergic synapse by RCSB PDB's Maria Voigt was selected as a national finalist in the 2021 Wiki Science Competition in the United States.
|
 |
G-Protein Coupled Receptors
Flyer
In honor of the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
|
| Glucagon-like Peptide-1 and Diabetes
Poster
Image of GLP-1 receptor recognizing a GLP-1 analog (yellow) with liraglutide.
|
|
 |
Insulin and Diabetes
Poster
Structural biology has revealed the details of insulin signaling and how this knowledge is being used to create new and better treatments for diabetes.
|
 |
Photoactive Yellow Protein and XFEL/SFX
GIF
Structures of photoactive yellow protein were determined by serial femtosecond crystallography after illumination, capturing the isomerization of the chromophore after it absorbs light. Structures included in this movie include: 5hd3 (ground state), 5hdc (100-400 femtoseconds after illumination), 5hdd (800-1200 femtoseconds), 5hds (3 picoseconds), 4b9o (100 picoseconds), 5hd5 (200 nanoseconds) and 1ts0 (1 millisecond). For more, see the Molecule of the Month on Photoactive Yellow Protein and Guide to Understanding PDB Data: Methods for Determining Atomic Structures
|
 |
How Neurons Communicate
Video
The billions of neurons in our nervous system are constantly communicating. The signals they send to each other are responsible for our thoughts, sensations, and actions. Learn how ions, ion channels, receptors, and neurotransmitters work together to enable the neuronal signaling process.
|
 |
Vitamin A and Vision
Video
Learn how vitamin A activates the molecular pathways that are essential for vision.
|
 |
Caffeine and Adenosine: Antagonist and Agonist
Video
This short video uses the example of adenosine and caffeine to introduce two key concepts in pharmacology: the agonist and the antagonist. Both, adenosine, and caffeine molecules bind to adenosine receptors on the neurons. Caffeine, the antagonist, blocks the receptor, while adenosine, the agonist, produces the biological response upon binding.
|
 |
Opioids and Pain Signaling
Video
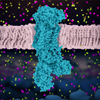
Pain is one of the most trying experiences of life. On the cellular level it is communicated via special neuronal pathways. On the molecular level, however, pain is communicated like any other sensation, via a set of electrical and chemical signals facilitated by complex molecular machinery. These signals can be modulated by opioids, causing us to feel less pain, or no pain at all. Learn how opioids activate the G-proteins which in turn interact with other proteins to edit the pain signal.
|
 |
Neuronal Signaling and Sodium-Potassium Pump
Video
Explore the concepts of resting and action potentials and the role of sodium-potassium pump in regulating them.
|
| Calcium Pump
Video
The calcium pump moves ions across cell membranes allowing the synchronized contraction of muscle cells.
|
|
 |
2021 Molecular Mechanisms of Drugs for Mental Disorders
Video
|
| 2020 Molecular Mechanisms of Opioid Action
Video
|
Curriculum Resources (1)
Structural Biology Highlights (15)
Global Health (1)
| Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Receptor
This is a membrane receptor that binds insulin and triggers a signaling cascade inside the cell, leading to glucose uptake and various other metabolic and growth-related functions.
|
Goodsell Molecular Landscapes (3)
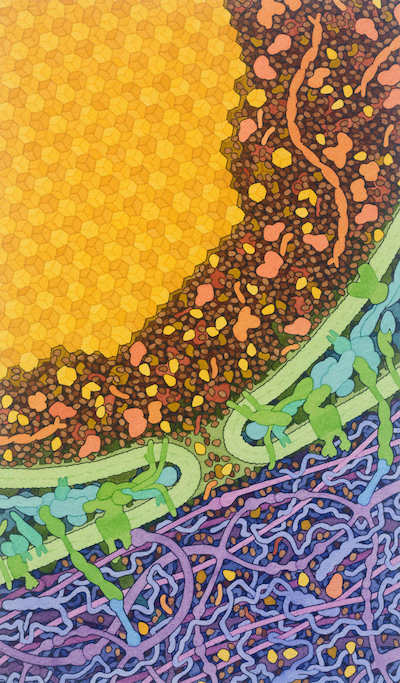 |
Insulin Release
Insulin is stored in small crystals inside pancreatic beta cells.
|
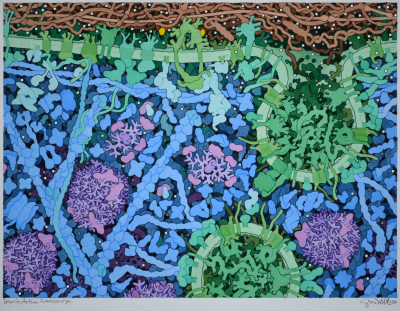 |
Insulin Action
Insulin Action (2016) by David S. Goodsell.
|
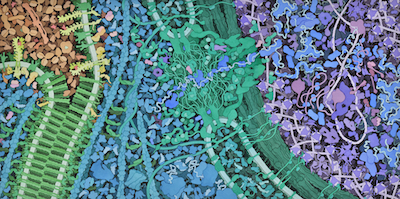 |
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VegF) Signaling
Cross section of two cells showing the VegF signaling pathway and some of its consequences.
|